Embark on a journey through the intricate world of database architecture, where every keystroke and design decision shapes the backbone of software development. This guide promises a detailed exploration of key components, types, design strategies, and maintenance tips that are crucial for building a scalable and efficient database architecture.
Introduction to Database Architecture
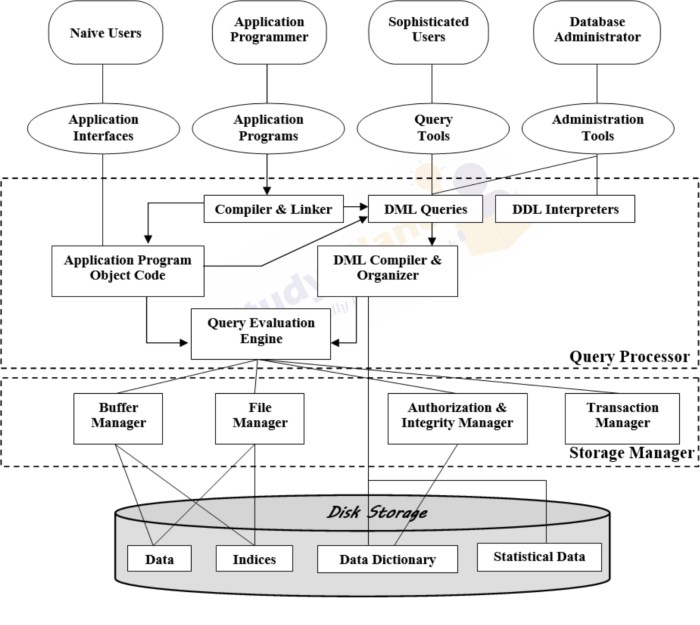
Database architecture refers to the design and structure of a database system, including how data is stored, organized, and accessed. It serves as the foundation for efficient data management and retrieval in software applications.The importance of database architecture in software development cannot be overstated.
A well-designed database architecture ensures data integrity, security, and performance, ultimately leading to a more reliable and scalable system. It also helps in optimizing queries, improving data access speed, and reducing redundancy.
Key Components of Database Architecture
- Data Model: Defines the structure of the data and how it is stored and accessed.
- Database Management System (DBMS): Software that manages the database, including data manipulation, security, and recovery.
- Database Schema: Represents the logical view of the entire database, including tables, relationships, and constraints.
- Indexing: Improves data retrieval speed by creating indexes on columns frequently used in queries.
Popular Database Architectures
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS): Uses tables to store data and SQL for querying, with examples like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- NoSQL Databases: Non-relational databases that offer flexibility and scalability, such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis.
- Big Data Architectures: Designed to handle large volumes of data, like Hadoop and Spark.
Types of Database Architecture

Relational and non-relational database architectures are two main types of database structures that serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
Relational Database Architecture
Relational databases store data in tables with rows and columns, where each row represents a unique record and each column represents a specific attribute. They use structured query language (SQL) to interact with the data. Relational databases ensure data integrity through normalization and relationships between tables.
Non-Relational Database Architecture
Non-relational databases, also known as NoSQL databases, store data in various formats like key-value pairs, document-oriented, column-family, or graph databases. They offer flexibility in handling unstructured or semi-structured data and can scale horizontally to manage large volumes of data.
Comparison and Contrast
- Relational Databases:
- Advantages:ACID compliance, strong consistency, mature technology, suitable for complex queries and transactions.
- Disadvantages:Limited scalability, slower performance for massive datasets, rigid schema design.
- Non-Relational Databases:
- Advantages:Flexible schema, horizontal scalability, better performance for large-scale distributed data, better suited for unstructured data.
- Disadvantages:Lack of ACID compliance, weaker consistency models, may require more complex data retrieval logic.
Use Cases
- Relational Databases:Excel in use cases requiring complex queries, data integrity, and transactional consistency, such as financial systems, e-commerce platforms, and traditional business applications.
- Non-Relational Databases:Ideal for scenarios demanding high scalability, fast data ingestion, and handling of varied data types, like real-time analytics, IoT applications, and content management systems.
Designing a Database Architecture
When it comes to designing a database architecture from scratch, there are several key steps and best practices to consider in order to create a scalable, efficient, secure, and high-performing database system.
Step 1: Define Requirements
Before diving into the design process, it's essential to clearly define the requirements of the database system. This includes understanding the data volume, types of data to be stored, access patterns, expected growth, and any specific performance or security needs.
Step 2: Data Modeling
Data modeling involves designing the structure of the database by identifying entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints. This step helps in organizing the data effectively and ensures data integrity and consistency.
Step 3: Choose the Right Database Management System (DBMS)
Selecting the appropriate DBMS based on the requirements and data model is crucial. Factors to consider include scalability, performance, security features, support for different data types, and ease of maintenance.
Step 4: Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to minimize redundancy and dependency. By breaking down data into smaller, manageable units, normalization helps in maintaining data integrity and reducing data anomalies.
Step 5: Indexing and Query Optimization
Creating indexes on frequently queried columns and optimizing queries can significantly improve database performance. Proper indexing and query optimization techniques help in speeding up data retrieval and processing.
Step 6: Backup and Recovery Planning
Implementing a robust backup and recovery strategy is essential to ensure data security and continuity in case of system failures or disasters. Regular backups, testing recovery procedures, and storing backups offsite are recommended best practices.
Step 7: Security Measures
Incorporating security measures such as user authentication, authorization, encryption, and auditing is critical for safeguarding sensitive data. Implementing access controls, monitoring database activity, and regularly updating security protocols are vital for maintaining data security.By following these steps and best practices, you can design a database architecture that is not only scalable and efficient but also optimized for performance, security, and data integrity.
Scaling and Maintenance of Database Architecture

Scaling a database architecture to handle growing data volumes presents several challenges as organizations accumulate more data over time. Techniques for horizontal and vertical scaling, along with regular maintenance and monitoring, are crucial to ensuring optimal performance.
Challenges in Scaling a Database Architecture
Scaling a database architecture to accommodate increasing data volumes can lead to challenges such as:
- Performance degradation as data grows, impacting query response times.
- Increased storage requirements and costs as more data is stored.
- Complexity in managing and maintaining a larger database infrastructure.
Techniques for Scaling a Database Architecture
There are two primary techniques for scaling a database architecture:
Horizontal Scaling:
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to distribute the workload and data across multiple machines. This approach helps improve performance and scalability by increasing capacity.
Vertical Scaling:
Vertical scaling involves upgrading the existing server with more resources, such as CPU, RAM, or storage capacity. While vertical scaling can provide a quick performance boost, it has limitations in terms of scalability.
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance and monitoring play a critical role in ensuring the health and performance of a database architecture. Key reasons for regular maintenance include:
- Identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks in a timely manner.
- Ensuring data integrity and security through regular backups and updates.
- Optimizing database performance through index optimization and query tuning.
Tools and Technologies for Managing and Scaling Database Architectures
Several tools and technologies are available to assist in managing and scaling database architectures, including:
- Database Management Systems (DBMS) like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle for database administration.
- Cloud-based solutions such as Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Microsoft Azure SQL Database for scalable and cost-effective database hosting.
- Monitoring tools like Prometheus, Nagios, and Datadog for real-time performance monitoring and alerting.
- Scaling solutions like Amazon Aurora, MongoDB Sharding, and Citus for horizontal scaling of databases.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering the art of database architecture is essential for ensuring optimal performance, security, and scalability of your data systems. By implementing best practices and staying abreast of evolving technologies, you can navigate the complexities of database architecture with confidence and finesse.
Common Queries
What is database architecture?
Database architecture refers to the design and structure of a database system, including its components, relationships, and organization of data.
How important is database architecture in software development?
Database architecture plays a critical role in software development by ensuring efficient data storage, retrieval, and management, impacting overall system performance.
What are the advantages of relational and non-relational database architectures?
Relational databases offer structured data storage and complex queries, while non-relational databases provide flexibility and scalability for unstructured data.
How can database performance be optimized through architecture design?
Optimizing database performance involves proper indexing, query optimization, efficient data storage strategies, and regular performance monitoring.
What tools are used for managing and scaling database architectures?
Tools like MySQL Workbench, MongoDB Atlas, and Amazon RDS are commonly used for managing and scaling database architectures.

